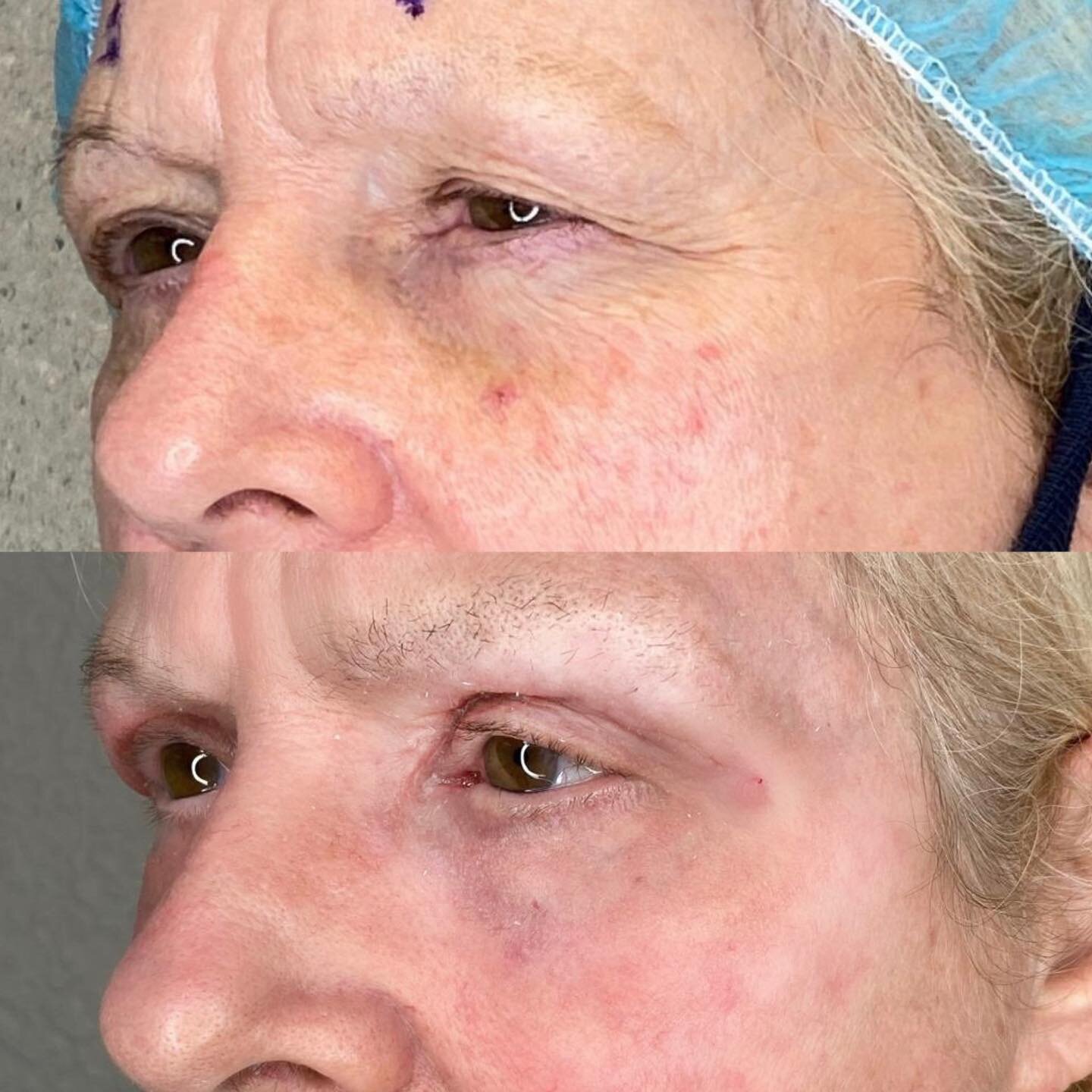
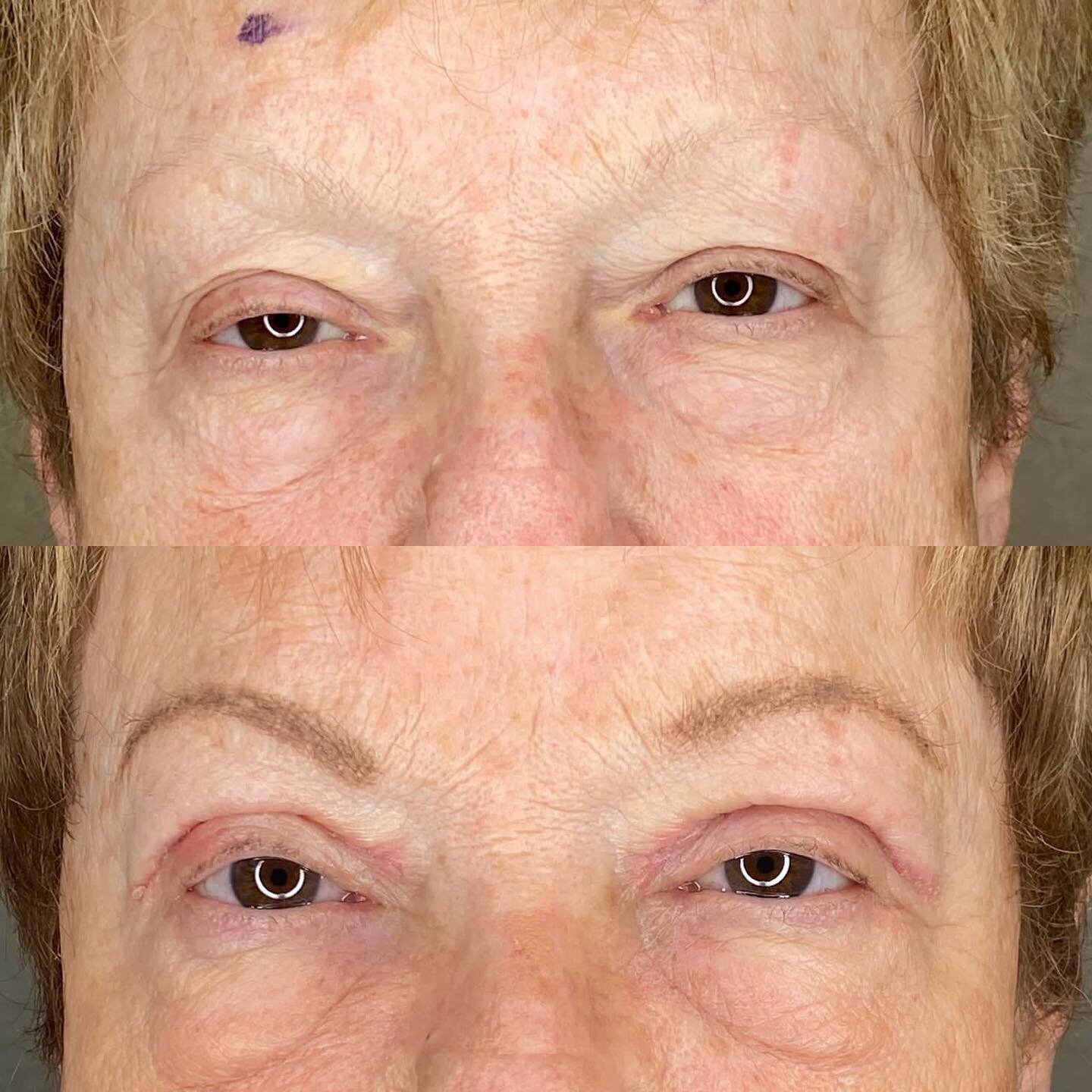
Cornea Surgery
Due to conditions such as scarring after injury or infections, keratoconus, a hereditary corneal failure, or any other condition resulting in glare or blurred vision, corneal surgery can be preformed to remove the damaged cornea and replace it with a clear donor cornea.
3 Steps to Better Vision
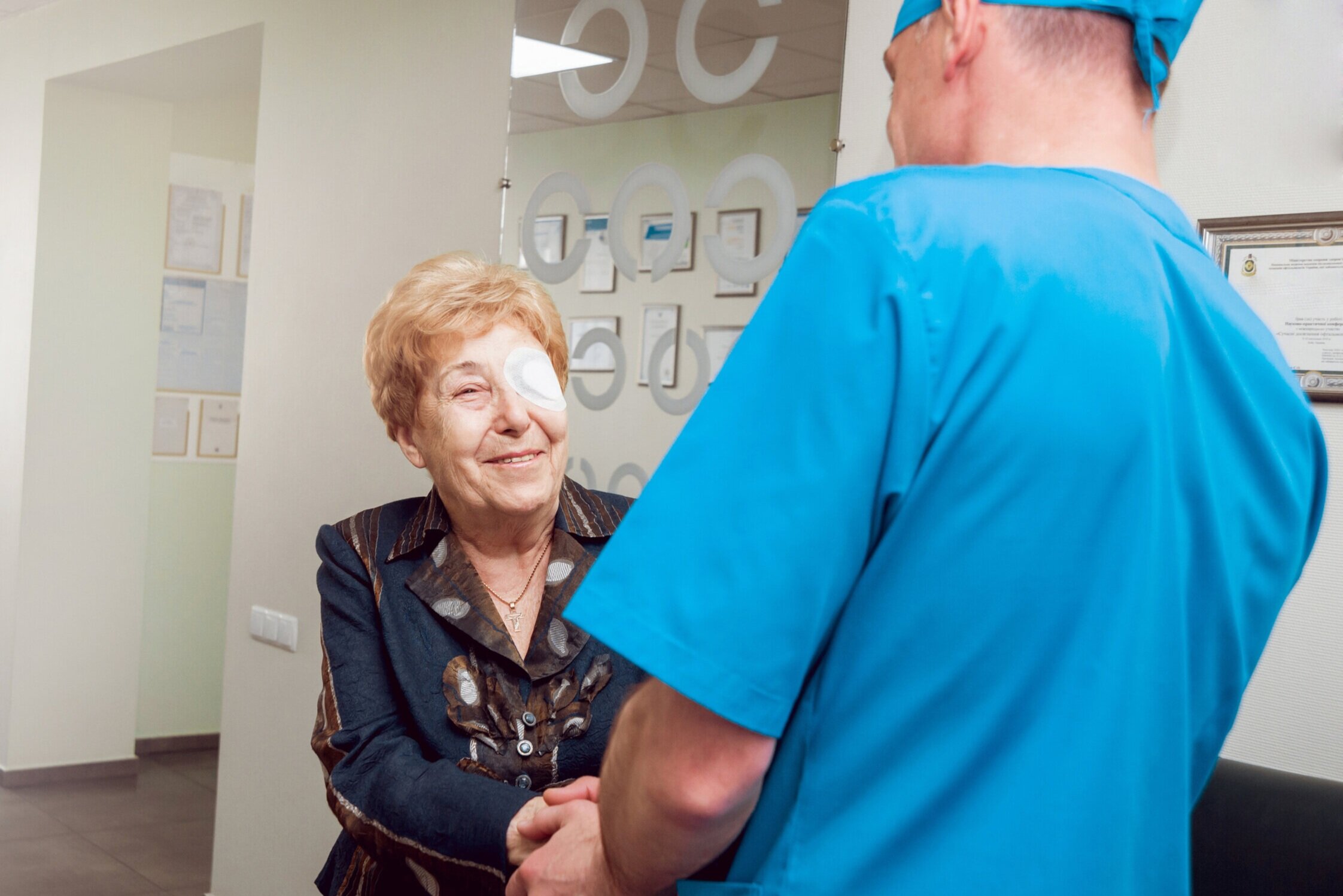
1. Arrival
After you arrive at the outpatient surgery center, your doctor will numb your eye with drops or an injection near the eye. Your doctor may also give you a medication to relax.
2. Surgery
Your surgeon will make tiny cuts with a laser or a blade near the edge of your cornea, which is the clear covering on the front of your eye. This will enable your surgeon to reach your cornea and begin repair.
3. Healing
In most cases, you will not need stitches to close the incisions. The so-called self-sealing incisions will close on their own in time. Your surgeon will place a shield over your eye to protect it during the healing process.
Frequently Asked Questions
Corneal Transplant
What is a corneal transplant?
A corneal transplant (keratoplasty) is a procedure in which some or all of a cornea in need of replacement is removed and replaced with donor tissue. The surgery may be done with traditional surgical technologies or with the aid of a surgical laser.
Why might I need a corneal transplant?
A corneal transplant may be necessary if you sustain a serious injury such as a deep scratch or burn. Clouding or repeated scarring of the corneal tissues over time may eventually obscure vision until you need surgery. Extremely thin corneal tissue caused by keratoconus may also require transplantation.
Where will my new cornea come from?
Regional facilities maintain tissue banks that include corneal tissue from individuals who have donated their corneas to medicine. The donor tissues are carefully inspected before surgery to make sure they are safe to use and appropriate for your eyes.
What are the different types of corneal transplant?
Endothelial keratoplasty replaces only the inner layer of your corneal tissue with donor tissue. A partial thickness corneal transplant replaces only the middle and outer layers. A penetrating keratoplasty (PK) replaces the full thickness of the corneal tissue.
What can I expect before and after my corneal transplant surgery?
Your surgery time will take about two hours, with time following in post anesthesia care to recover. Some redness, tearing, light sensitivity, and irritation for a few days after your surgery are to be expected. You will be given an eye shield that will protect your treated eye during sleep while it recovers. Eye drops and ointments will be prescribed to protect the eye from complications.
How successful are corneal transplants?
Due to the avascular nature of the cornea, most corneal transplants are highly successful and last for many years. Some people may experience tissue rejection, in which case another transplant may be necessary.
How can Perich Eye Center help?
We can advise you when it’s time to consider a corneal transplant and counsel you on the procedure and after care. We can also co-manage your recovery through regular eye and vision exams. We are proud to have many years of expert experience caring for patients with corneas.
DSAEK
What is DSAEK surgery?
DSAEK, which stands for decimates stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty, is a partial-thickness corneal transplant that replaces only the innermost layer of the cornea. DSAEK is a relatively new surgical technique that affords significant improvements over traditional corneal transplants for certain indications. The surgery itself takes less time, involves a smaller surgical incision, requires minimal stitches, has a shorter healing time, and a faster visual recovery.
Where Is the DSAEK procedure performed?
We perform DSAEK procedures here at Perich Eye Center in our surgery center.
The total time the patient will be in the surgery center is approximately 2 to 4 hours. Once the patient is taken to the operating room, the procedure is completed in 20 to 30 minutes.
Additional time may be necessary if other procedures are also planned, like cataract surgery or intraocular lens replacement. After your procedure is completed you will be taken to the recovery room where you will lie on your back for 45 to 60 minutes. This allows the air that has been placed in the anterior chamber of their eye to secure the new transplant into position.
What can I expect during a DSAEK Procedure?
DSAEK surgery is performed as an outpatient procedure. Although you will not be asleep during the procedure, you will be given sedation and a local anesthetic to keep you comfortable the entire time. One of our surgeons will make a small incision comparable to that made during cataract surgery. An instrument is then used to remove the diseased inner layer of the cornea. The healthy inner layer of an organ donor cornea is then inserted into the eye and maintained in place with the use of an air bubble that is left in the eye. During the surgery, you may feel pressure around the eye, but not pain. After the procedure, a patch will be placed over the eye and you will return home where you are instructed to rest for the remainder of the day, lying flat on your back to keep the air against the corneal transplant.
How long does It take to recover after DSAEK surgery?
Your vision will be quite blurry for the first few weeks after surgery as the new cornea is healing. To follow up, repeated visits will be necessary to monitor the progress of the transplant. The total visual recovery time for a DSAEK surgery is typically between two to six months. Occasionally, the transplant may “detach” from the more superficial layers of the cornea and the transplant would have to be repositioned. Other times, the transplant may fail and would have to be replaced. If the DSAEK fails, either after one or multiple attempts, a traditional corneal transplant operation can still be performed. Similar to other organ transplants, anti-rejection medications are required for a number of years— however, rather than pills, eye drops are used for this purpose.
When will I need to return for a follow-up visit after my surgery?
The first office visit is scheduled about 1.5 to 2 hours after the DSAEK procedure has been completed. After leaving the surgery center you will be taken to my office. The visit is necessary so that I can remove the air that was placed in your eye. Since your eye is still totally numb you will not experience any pain while I remove the air. Removal of the air only takes a few seconds and is necessary so that you do not experience an intraocular pressure spike during your first evening. You will also return for a follow-up visit the next morning after DSAEK surgery. During this visit, the health and position of the new transplant will be checked. If everything is in proper order you will start your post-op eye drops as directed and return for a follow-up visit in 1-2 weeks.
What types of eye drops will I be given to take after my surgery?
You will continue using the antibiotic eye drops (Besivance) that you started three days prior to surgery. Use the Besivance 4x per day for one week after surgery unless otherwise instructed. You will also use a steroid eye drop (Omnipred 1% or Pred Forte) 4x per day until otherwise instructed. The steroid drops are required to prevent rejection of your new transplant. If you are also using glaucoma eye drops, please also continue to use them after surgery unless otherwise instructed by your doctor.
When will I see improvement in my vision?
Visual recovery varies depending on the severity of your corneal cloudiness prior to surgery. Most patients notice improvement in their vision during the first two weeks after surgery, with continued improvement during the next four to six weeks. This recovery represents a dramatic improvement over the time required following conventional corneal transplant surgery (PKP), which usually takes six to twelve months. Some DSAEK patients may not notice visual improvement as quickly as they would like, because they have other ocular conditions such as a cataract or retinal problems that must be addressed.
What is the risk my body will reject the DSAEK?
Although the rate of rejection with DSAEK does not appear to be any higher than rejection rates with PKP, endothelial rejection is still something to look out for. The signs and symptoms of such rejection episodes are the same as they are for PKP patients. As a rule of thumb, if you experience redness, photophobia, and blurred vision we want you to assume that you are having a rejection episode, and for you to call our office so that you can be evaluated immediately. Most rejection episodes are successfully terminated by using steroid eye drops. The sooner a rejection is treated, the better chance for transplant survival.
Pterygium Surgery
What is Pterygium Surgery?
Pterygium surgery is a procedure performed to remove noncancerous conjunctiva growths (pterygia) from the eye. The conjunctiva make up the clear tissue covering the white part of the eye and the inside of the eyelids. Some cases of a pterygium produce little to no symptoms, however severe overgrowth of conjunctiva tissue can cover the cornea and interfere with your vision.
How Long Will My Cornea Pterygium Surgery Take?
Pterygium surgery is a minimally invasive surgery, that generally takes no more than 30 to 45 minutes. Before your surgery date we will provide you with general guidelines to help you feel prepared. You will be required to fast or only eat a light meal beforehand. In addition, if you wear contact lenses, you will be asked to not wear them for at least 24 hours before the procedure. Because you’ll be lightly sedated, doctors will require you to arrange transportation after the surgery, as you’ll be unable to drive yourself.
What to expect during pterygium surgery?
The pterygium surgical procedure is fairly quick and low risk.
We will sedate you and numb your eyes to prevent discomfort during surgery, and will then clean the areas surrounding your eye.
We will then remove the pterygium along with some associated conjunctiva tissue.
Once the pterygium is removed, we will replace it with a graft of associated membrane tissue to prevent recurrent pterygium growths.
What happens after my pterygium surgery?
Once the pterygium is removed, we will either use sutures or fibrin glue to secure the conjunctiva tissue graft in its place. Both techniques reduce the possibility of recurring pterygia. While using dissolvable sutures may be considered a benchmark practice, it can cause more discomfort post surgery, and extend the recovery time for several weeks. We will discuss whether using traditional sutures versus fibrin glue suture are appropriate for you.
How long does it take to recover after pterygium surgery?
At the end of surgery, your doctor will apply an eye patch or pad for comfort and to prevent infection. It’s important to not rub your eyes after the procedure to avoid dislodging the attached tissue.
We will provide you with aftercare instructions, including cleaning procedures, antibiotics, and scheduling follow-up visits.
Recovery time can take anywhere between a couple of weeks to a couple of months for your eye to completely heal, without signs of redness or discomfort. However, this may also be dependent on the type of technique used during surgery.
What are the risks associated with my pterygium procedure?
Following the pterygium surgery, it’s normal to experience some discomfort and redness. It’s also common to notice some blurriness during recovery. However, if you begin to experience vision difficulties, a complete loss of vision, or notice pterygium regrowth, schedule a visit to your doctor.